
Car and Motorcycle MOT - What's Tested?
Car MOT Checklist
Registration plates, tow bar and Vehicle Identification Number* (VIN).* Required on all vehicles first used on or after 1st August 1980. NOTE: Revised Registration Plate Testing and Tow Bar Testing (see below) were effective from April 09.
(See current Number Plate Regs graphic.)
For registered vehicles the registration plate must be:
- Present
- Secure
- Not faded, dirty or obscured
- Be composed with correctly formed letters and spacing
Registration Plate Specifications.
| Relevant Dimension | Tricycles & quadricycles | All other vehicles |
| Character Height | 64mm | 79mm |
| Character width (except for the figure 1 or letter I) | 44mm | 50mm |
| Stroke Width | 10mm | 14mm |
| Space between two characters in group | 10mm | 11mm |
| Vertical space between groups of characters | 13mm | 19mm |
| Horizontal space between groups of characters | 30mm | 33mm |
| Margins(minimum) | 11mm | 11mm |
- Permanently displayed
- Consistent
- Legible
Reason for Rejection:
A towbar component insecure, fractured or excessively:
- Worn
- Corroded, or
- Damaged
- Towbar assembly is attached to the vehicle structure using a mounting, support or fixing which is obviously of an inappropriate size or type
- Retaining device missing or insecure
- Locking device missing, insecure, inadequate or damaged to the extent that its operation is impaired
- Excessive play between a detachable tow ball and its receiver socket
- A quick release mechanism that does not secure the tow ball arm as intended
Inside the car checks.
Steering wheel and steering column:
- Steering wheel is in acceptable condition
- Steering wheel is securely attached to the steering shaft
- Upper bearings of the steering column are inspected for wear
- Steering shaft is checked for excessive end float
- The clamping bolts are all checked for security
- Split pins and locking nuts are also checked
- 'Free play' in the steering is checked*
- All flexible couplings and universal joints are checked
Reasons for failure:
1. Steering wheel weakened by modification, cracks, fractures, in a condition that hampers proper control or likely to injure the driver's hands.Note: Cracks or incompleteness of the covering skin of a steering wheel or hub, are not a reason for rejection.
2. a) An adjustable steering column will not lock in a fixed position
b) Movement between the shaft and steering wheel
c) Excessive radial movement (play) at the top of the steering column between the column and the shaft indicating a badly worn top bearing.
Note: Some vehicles have flexible top bearings for the steering column. With these more than average movement is acceptable.
d) Insecurity at the steering column top mounting bracket.
3. Excessive steering shaft end float.
4. Insecurity, excessive play or deterioration of a flexible coupling or universal joint.
5. A retaining or locking device missing or insecure.
Under bonnet checks
This varies vehicle to vehicle; some of these items cannot be observed from under the bonnet on some makes and models.
- Security of the steering rack or steering box and its mountings
- Play in steering joints
- Inspection of any other swivel joints which form part of the vehicles' steering system which can be readily inspected from under the bonnet
- All the steering joints are inspected by the Tester whilst the steering is loaded by turning the steering wheel from side to side
- Power steering systems are checked with the engine running
- The security of attachment of the steering rack or steering box is checked both with respect to the tightness of nuts and bolts, and structural cracking or corrosion of the vehicle chassis where it is attached
- Whilst the vehicle stands on special swivel plates the wheels are turned from lock to lock and checked to ensure that the wheels and tyres do not foul either the structure of the vehicle or any brake pipes or hoses
- With the wheels jacked the wheel bearings are checked
- Steering rack gaiters and front outer constant velocity joint boots are examined
- Metal and/or rubber bushes are checked as are split pins, locking nuts and other locking or retaining devices which relate to steering components
- On some cars there will be rear wheel steering which is checked from beneath the car
Horn
- Operation
- Control can be easily reached by the driver
- Loud enough
- Not a sequential multi-tone
Lights
Test Description
The headlamps are checked for alignment with a Beam Setter. After first aligning the equipment with the vehicle, the left and right headlamp beams are checked to ensure they are correctly set so as not to dazzle other road users.
All required lights are checked for:
- Operation
- Condition
- Security
- Are the correct type and colour
- Dip and aim
Stop lights, indicators and hazard lights*
- Are the correct type and colour
- Do not interfere with each other in operation
- Driver's tell-tale works with respect to indicators, or there is an audible warning system
- Must be fitted to the centre or offside of the vehicle
- Tell-tale must work
- Must not be affected by other lamps and not be obscured
- Must be red
- All lamps fitted must be working
- There must be two red reflectors fitted reasonably symmetrically, securely attached and not obscured
** Must be fitted to all vehicles first used on or after 1st April 1980.
Bonnet Catch
Reasons for Failure
- A bonnet that cannot be safely secured in the closed position
- An excessively deteriorated, ineffective or insecure (bonnet) retaining device
Doors
Test Description
Both front doors must be openable from the inside and outside and all doors must latch securely.
Tailgates, bootlids etc
All these items, including the tailboards and dropsides of trucks must be securable in the closed position.
Vehicle Structure
Body condition and security
- Body must not be so insecure or displaced so that it might lead to loss of control of the vehicle when driven, or be a danger to other road users
- There must be no dangerous sharp edges or projections caused by corrosion or damage which is dangerous to other road users including pedestrians
A vehicle can fail with respect to corrosion for:
- Excessive corrosion in a 'prescribed area' — within 30 cms of certain safety related components, e.g. brakes, steering, suspension, seat belt mountings etc
- Excessive corrosion not in a 'prescribed area', but which is likely to adversely affect the vehicle's braking or steering. 'Excessive corrosion' can mean a hole or a significantly weakened structure
Seats
The driver's and the front passenger's seats must be secure.
All seat backs must be securable in the upright position.
Seat Belts
Test Description
Most vehicles after 1965 must have seat belts. Irrespective of that requirement, all seat belts fitted to any vehicle must be inspected for:
Notes:
1. For technical reasons the inertia locking mechanism is not checked.
2. On some vehicles the belt is attached to the seat, in which case the security of the seat to the vehicle would also constitute part of the seat belt check.
Brakes
Test Description
Brake efficiency and balace is usually checked on a roller brake tester. In certain cases where a roller brake tester may not be used (for example on certain 4-wheel drive vehicles) it may be necessary to check brake efficiency and balance on a road test, with a portable decelerometer.
Inside the car
Anti-lock braking system (if fitted) warning lamp is checked for:
- Function
- Sequence of operation
Footbrake
- Sufficient reserve travel on the footbrake
- Pedal rubber not worn to excess
- Correct operation of the servo assistance system
Parking brake
This could be hand or foot operated. Checked for reserve travel so that it doesn't reach the stops on application. The mountings will be checked for security and/or corrosion.
Under bonnet checks
- Master cylinder and servo unit are checked for leaks with the engine on and the brakes applied
- Servo unit will be checked to ensure it is operating correctly
- Visible metal or flexible brake pipes will be checked for corrosion, condition, fouling or leaks
Under vehicle checks
- Flexible brake pipes and any other metal brake pipes visible beneath the car are checked
- Discs and drums (external only) checked for condition and contamination
- Brake back plates and caliper securing devices are checked for condition and security
- Condition of the brake pads will be checked if visible
- The assistant operates the handbrake and the condition of the linkages and/or cables is checked
- On some vehicles there will be a brake compensating valve beneath the car which will need to be inspected for fluid leaks
Brake performance check
The performance of the front and rear brakes and handbrake are checked for efficiency and balance using specialised equipment.
Windscreen
Includes all items affecting the driver's view of the road: the condition of the windscreen, the wipers and washers.
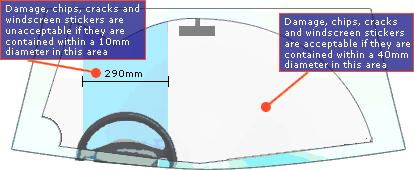
Chips or cracks in the windscreen directly in front of the driver, in the area swept by the wiper blades, are acceptable if they are less than 10mm in diameter. In the rest of the swept area, up to 40mm diameter damage is acceptable.
Official stickers (any used in connection with road enforcement, security or crime prevention matters) that are not readily removable are only a reason for rejection if they restrict the driver's view.
Washers and wipers
- Operation
- Extent of area swept by the wipers
- Condition of the wiper blades
Mirrors
Not all mirrors on all vehicles are subject to Test, depending on the age of the vehicle. Those mirrors which must be checked must be:
- Secure
- Visible from the driver's seat
- Not distorted or damaged so as to seriously impair the driver's view to the rear
Suspension
Test Description
Under bonnet checks
upper suspension joints
- any other suspension components which can be inspected from beneath the bonnet
Under vehicle checks
Applies to the front and rear suspension
- No split pins or nuts missing, no components broken or excessively damaged
- Road springs are checked for condition
- All suspension joints are checked for condition
- Shock absorbers must not leak and must be secure (the vehicle will be 'bounced' by the Tester to check that they damp the springs adequately)
The suspension is checked for wear by the assistant applying loads in various ways with the wheels jacked up whilst the Tester observes the result from beneath the vehicle.
Note: There are numerous different suspension systems, and the specific nature of any examination will depend to a large extent on the design of the suspension system.
Exhaust system and Emissions
Test Description
The exhaust system will fail the MOT if:
- Part of the system missing or excessively deteriorated
- A mounting is missing or damaged so it does not support the system
- There is a major leak
- The system is excessively noisy
Emissions
These are checked using specialised equipment, the details of the check depending on the year that the vehicle was first used on the road. Excessive smoking (checked visually) is a reason for failure.
Diesel smoke emissions are checked by using a smoke meter. Fuel system Any fuel leak will result in a fail. Checked under the bonnet and throughout the run of the fuel line from the fuel tank to the engine.
- Fuel filler cap must fasten securely
- The seal in the cap must not be torn, deteriorated or missing
- No other defect which could cause fuel to leak out
Tyres and Roadwheels condition
Tyre condition
The reason for failure with respect to tyre wear is:
"The grooves of the tread pattern are not at least 1.6mm throughout a continuous band comprising: the central three-quarters of the breadth of tread around the entire outer circumference of the tyre".
Tyres must be correctly matched with regard to:
- Type
- Size
- Structure
NB. type or structure but not both.
- Tyres on the same axle must be of the same structure and size
Also examined:
- General condition of tyre
- Condition of valve
Tyres fail if they have serious cuts, bulges or other damage.
The wear on the tyre is checked with a tyre tread depth gauge to ensure compliance.
The tyres are examined to ensure that there is no fouling with any part of the vehicle.
Notes: Although under-inflation is not in itself a reason for failure, a brake test may be inadvisable because of possible damage, and it may affect headlamp alignment. The condition of the spare tyre is not part of the MOT.
Wheel condition
- Damage
- Distortion
- Cracks
- Distorted bead rim
- Securely attached to the vehicle
- No wheel nuts or studs missing
An externally fitted spare wheel or spare wheel carrier must not be so insecure that it is likely to fall off.
Motorcycle MOT Checklist
a) Sitting on machine check:1. All controls, switches and horn
2. Front suspension, forks, handlebars and head bearings
b) At the front of the machine check:
1. Front lights and indicators
2. Front brake master cylinder (if fitted)
c) Place the machine on its stand and raise front wheel check:
1. Steering, front forks and head bearings
2. Front brake and wheel bearings
3. Wheel and tyre condition
d) Lower front wheel and go to right side of vehicle and check:
1. Frame, VIN, seat and foot rest
2. Exhaust system
3. Final drive (if fitted to RHS of machine)
4. Rear wheel, tyre and brake
e) Raise the rear wheel and check:
1. Rear wheel, rear brake/components and tyre condition
2. Rear suspension and final drive
f) At the rear check:
1. Rear position lamp(s)/stop lamp(s)/reflectors and indicators
2. Rear suspension
3. Registration Plate
g) On the left of the machine check:
1. Frame and foot rest
2. Exhaust system
3. Final drive (if fitted to LHS of machine)
4. Rear wheel, tyre and brake
h) At the front of the machine check:
1 Wheel alignment
2 Headlamp aim
3 Brake performance
If a sidecar is fitted it will also be examined in a manner specified by VOSA with respect to Security, Suspension, Wheel Bearings and Wheel Alignment.



